"Useless" Box - Grade 11 Coding
During my grade 11 coding course, we were given the freedom to choose a project, and my team enthusiastically decided to create a “useless” box, a whimsical device that deactivates itself when clicked. Leveraging a Raspberry Pi board and a relay, we embarked on a journey that not only resulted in a fun and quirky creation but also provided invaluable insights into coding, hardware integration, and prototyping.
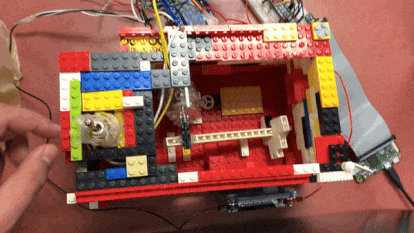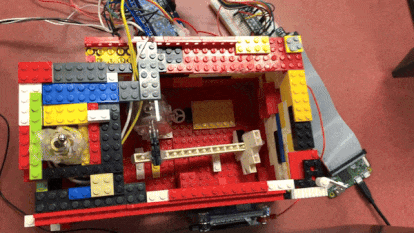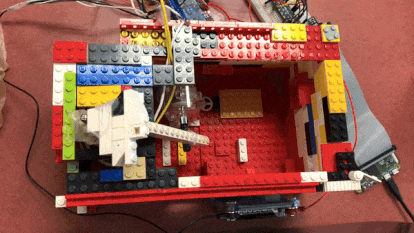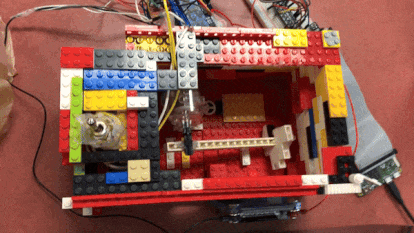
The “Useless” box in action
Key Contributions:
- Hardware Connections:
-
Took charge of making all the necessary connections, ensuring seamless integration of the Raspberry Pi board and the relay.
-
Acquired hands-on experience in hardware assembly and learned the essentials of interfacing different components.
-
- Python Code Development:
-
Wrote Python code for the Raspberry Pi, orchestrating the relay to activate and deactivate at specific times.
-
Gained proficiency in coding for hardware control, understanding the basics of motor control through the relay.
-
Key Learnings:
- Motor Control Basics:
-
Mastered the fundamentals of controlling a motor using a relay, laying a foundation for more advanced robotics projects.
-
Acquired practical knowledge of GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) programming for hardware interaction.
-
- Prototyping Skills:
-
Delved into the world of prototyping, understanding the importance of iterative development and troubleshooting.
-
Developed problem-solving skills by overcoming challenges in the hardware and software integration process.
-
Future Implications:
The “useless” box project was not just a playful exploration but a valuable stepping stone for my future in robotics. The skills acquired in hardware connections, coding, and prototyping have set the stage for more complex and impactful endeavors in the field.
Conclusion:
Creating the Raspberry Pi-controlled “useless” box in my grade 11 coding course was a delightful and educational experience. Beyond the amusement of the project, I gained practical insights into hardware integration, coding for motor control, and the iterative process of prototyping. These skills are not only applicable in robotics but also lay the groundwork for a future filled with innovative and meaningful contributions to the field.